With the increasing complexity of smart contracts, crypto wallets are finding it increasingly difficult to decipher their contents, forcing users to sign transactions without knowing the details.
This practice, called blind signing, is gradually becoming the norm in the cryptocurrency industry, at the expense of investor security.
Learn what blind signing is and how it affects the security of your cryptocurrencies.
This practice is particularly common in transactions involving smart contracts , autonomous computer programs whose execution does not require the intervention of a trusted third party.
Smart contracts now govern the majority of blockchains and are ubiquitous in user interactions.
However, the constant evolution of decentralized applications (DApps) constantly complicates their code, making them increasingly difficult to be interpreted by wallets.
Crypto wallets , or wallets (the entities responsible for supporting users in their on-chain activity), are responsible for decrypting these smart contracts during their use in order to protect users. So, when you want to interact with one of them, your wallet informs you of its contents and what you are about to approve.
However, with the growing complexity of smart contracts, crypto wallets struggle to decipher their contents, forcing you to approve a transaction whose terms you don't know. Here's an example highlighting the differences between a blind signature and a plaintext signature.
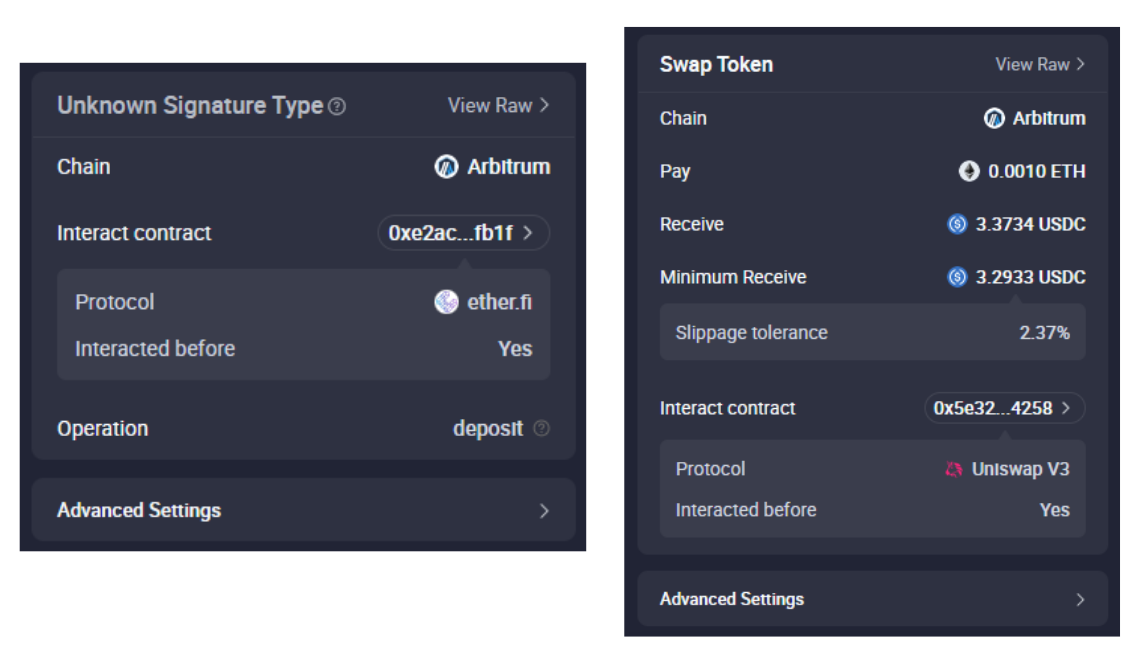
On the left, here's an example of a blind signature. The requested signature type is displayed as " Unknown ," and very little information is provided about the smart contract's actions except for the operation type, " deposit ," which simply corresponds to the name of the called function (its content can be anything else). Conversely, in the plaintext signature example on the right, the terms of the smart contract are explicit and detailed.
Blind signing, while posing risks to users, isn't necessarily a scam, but is simply the result of your crypto wallet's inability to detect smart contract information. Indeed, blind signing is common when interacting with DApps.
If you're a fan of decentralized finance (DeFi) , you've probably already signed a contract blindly, without getting scammed.
The same principle applies in the world of cryptocurrencies. When you sign a transaction from your crypto wallet to interact with a smart contract, you agree to abide by the smart contract's terms. And if you can't read the smart contract's terms, how can you be completely sure it's not malicious? The answer is simple: you can't.
Therefore, when you blindly sign an interaction with a smart contract, the security of your cryptocurrencies relies in some way on the trust you have in the entity that offers it to you.
Hackers consider blind signatures to be an exploitable flaw . They create malicious smart contracts that they try to trick you into interacting with without you being able to verify their contents, potentially resulting in the total loss of your crypto. Therefore, it's important to adopt best practices to protect yourself against this type of scam.
Thus, the display of the transaction that caused the hack appeared legitimate on the wallet's web interface, while the real contents of the transaction were sent to the hardware wallets of ByBit signers.
Thinking it was a legitimate transaction, they signed the transaction on their hardware wallet without knowing its actual contents, leading to the loss of $1.5 billion in ETH.
How to protect yourself against blind signing scams?
According to on-chain security specialists PeckShield, nearly $3 billion in crypto was stolen by hackers in 2024. It is therefore essential to protect against any potential breaches, including blind signing.
To protect yourself from blind signing scams, it is recommended to follow these points:Read the terms of the smart contract . Before signing a transaction, always read its details to understand the actions the smart contract will perform, and check that they correspond with what you want to do (swap, staking, etc.). For example, in the case of a transaction on a cryptocurrency bridge, check that the destination address of your cryptos is the one you requested and that it has not been modified by the smart contract (which can happen in the event of a bridge hack);
Detect if you are dealing with a blind signature . Wallets by default attempt to provide you with the details of the smart contract you are interacting with. If your wallet does not make the details of the interaction with the smart contract explicit, then you are about to perform a blind signature!
Only interact with recognized protocols . If you are required to blind sign, make sure you are using a popular protocol that is widely used enough that you can trust its smart contracts;
Use crypto wallets that protect you . Ledger hardware wallets disable blind signing by default. Additionally, some browser wallets like Rabby automatically alert you about the popularity of the smart contracts you're trying to interact with.
Obviously, this list is not exhaustive and only concerns scams related to blind signatures. To learn more about security in the cryptocurrency ecosystem, don't hesitate to consult our guide to 7 best practices to follow to protect your crypto wallet .
Indeed, today, most crypto wallets do not explicitly indicate when a transaction involves blind signing, and the majority of investors do not thoroughly review their transactions before signing them. This explains why the practice of blind signing often goes unnoticed by users.
However, blind signatures require the user to trust the issuer of the smart contract, which runs counter to the values proposed by blockchain. Indeed, a famous saying within the crypto ecosystem expresses this perfectly: "Do n't trust, verify. " In other words, the user should always have the ability to verify, including the content of the transactions they are about to sign.
What is blind signing?
In the world of cryptocurrencies, blind signing is the act of signing a transaction from one's wallet without knowing its full contents .This practice is particularly common in transactions involving smart contracts , autonomous computer programs whose execution does not require the intervention of a trusted third party.
Smart contracts now govern the majority of blockchains and are ubiquitous in user interactions.
However, the constant evolution of decentralized applications (DApps) constantly complicates their code, making them increasingly difficult to be interpreted by wallets.
Crypto wallets , or wallets (the entities responsible for supporting users in their on-chain activity), are responsible for decrypting these smart contracts during their use in order to protect users. So, when you want to interact with one of them, your wallet informs you of its contents and what you are about to approve.
However, with the growing complexity of smart contracts, crypto wallets struggle to decipher their contents, forcing you to approve a transaction whose terms you don't know. Here's an example highlighting the differences between a blind signature and a plaintext signature.

Example of blind signature (left) and clear signature (right) on the Rabby wallet
On the left, here's an example of a blind signature. The requested signature type is displayed as " Unknown ," and very little information is provided about the smart contract's actions except for the operation type, " deposit ," which simply corresponds to the name of the called function (its content can be anything else). Conversely, in the plaintext signature example on the right, the terms of the smart contract are explicit and detailed.
Blind signing, while posing risks to users, isn't necessarily a scam, but is simply the result of your crypto wallet's inability to detect smart contract information. Indeed, blind signing is common when interacting with DApps.
If you're a fan of decentralized finance (DeFi) , you've probably already signed a contract blindly, without getting scammed.
What is the danger of blind signing?
The practice of blind signing presents a significant source of danger for crypto wallet users . Indeed, in the real world, a contract is a document spelling out the terms under which two parties agree. Signing a contract obligates you to abide by its terms.The same principle applies in the world of cryptocurrencies. When you sign a transaction from your crypto wallet to interact with a smart contract, you agree to abide by the smart contract's terms. And if you can't read the smart contract's terms, how can you be completely sure it's not malicious? The answer is simple: you can't.
Therefore, when you blindly sign an interaction with a smart contract, the security of your cryptocurrencies relies in some way on the trust you have in the entity that offers it to you.
Hackers consider blind signatures to be an exploitable flaw . They create malicious smart contracts that they try to trick you into interacting with without you being able to verify their contents, potentially resulting in the total loss of your crypto. Therefore, it's important to adopt best practices to protect yourself against this type of scam.
The $1.5 billion ByBit hack example
On February 21, 2024, crypto platform ByBit suffered a nearly $1.5 billion hack through a blind signature attack . Using social engineering techniques, attackers managed to modify the front-end of the multisignature wallet Safe{Wallet} used by ByBit.Thus, the display of the transaction that caused the hack appeared legitimate on the wallet's web interface, while the real contents of the transaction were sent to the hardware wallets of ByBit signers.
Thinking it was a legitimate transaction, they signed the transaction on their hardware wallet without knowing its actual contents, leading to the loss of $1.5 billion in ETH.
How to protect yourself against blind signing scams?
According to on-chain security specialists PeckShield, nearly $3 billion in crypto was stolen by hackers in 2024. It is therefore essential to protect against any potential breaches, including blind signing.
To protect yourself from blind signing scams, it is recommended to follow these points:Read the terms of the smart contract . Before signing a transaction, always read its details to understand the actions the smart contract will perform, and check that they correspond with what you want to do (swap, staking, etc.). For example, in the case of a transaction on a cryptocurrency bridge, check that the destination address of your cryptos is the one you requested and that it has not been modified by the smart contract (which can happen in the event of a bridge hack);
Detect if you are dealing with a blind signature . Wallets by default attempt to provide you with the details of the smart contract you are interacting with. If your wallet does not make the details of the interaction with the smart contract explicit, then you are about to perform a blind signature!
Only interact with recognized protocols . If you are required to blind sign, make sure you are using a popular protocol that is widely used enough that you can trust its smart contracts;
Use crypto wallets that protect you . Ledger hardware wallets disable blind signing by default. Additionally, some browser wallets like Rabby automatically alert you about the popularity of the smart contracts you're trying to interact with.
Obviously, this list is not exhaustive and only concerns scams related to blind signatures. To learn more about security in the cryptocurrency ecosystem, don't hesitate to consult our guide to 7 best practices to follow to protect your crypto wallet .
Should we be worried about the widespread use of blind signing?
The practice of blind signing is increasingly widespread in the crypto ecosystem, putting the security of users' funds at risk. However, its widespread adoption is not controversial.Indeed, today, most crypto wallets do not explicitly indicate when a transaction involves blind signing, and the majority of investors do not thoroughly review their transactions before signing them. This explains why the practice of blind signing often goes unnoticed by users.
However, blind signatures require the user to trust the issuer of the smart contract, which runs counter to the values proposed by blockchain. Indeed, a famous saying within the crypto ecosystem expresses this perfectly: "Do n't trust, verify. " In other words, the user should always have the ability to verify, including the content of the transactions they are about to sign.





0 Comments